UNDERSTANDING STEM CELLS: BACKGROUND, FUNCTIONS AND EFFECTS
Stem cell therapy is on the cutting edge of modern medicine. But what are stem cells? Stem cells are active in each person, a lifetime long. They divide and multiply and play an essential role in the constant process of renewal which takes place in the human body. Therefore, stem cells help us to stay healthy by regenerating depleted or injured tissue.
The principle is quite simple – and at the same time ingenious: Stem cells are a type of genesis-cell, and have the ability to divide and produce different sorts of body tissue. This is a unique characteristic of stem cells. Normal cells hardly charge during their life-cycle. However, stem cells retain the ability – and the duty – of continuing development and generating diverse tissue and organ cells.
STEM CELL ABILITIES
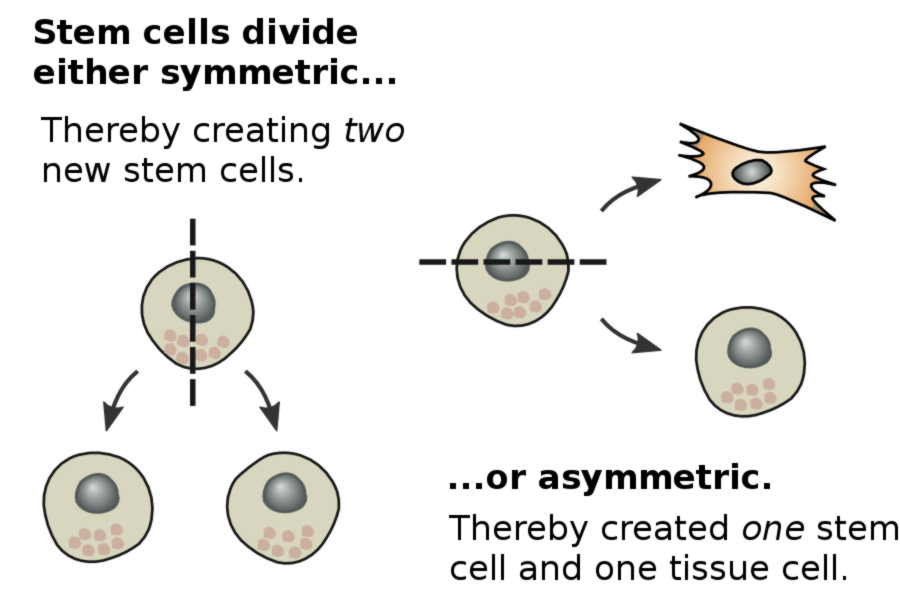
Stem cells have two key capabilities: Self-renewal (symmetrical division) and differentiation (asymmetrical division). During symmetrical division, stem cells are created which are identical to the parent cell. During asymmetric division, only one stem cell is created – in the second cell, tissue cell development and differentiation has already begun. Symmetrical division makes stem cells virtually immortal: it continually produces new stem cells in an almost unlimited number. Asymmetric division makes the reconstruction and repair of organs possible by generating new cell tissue.
DIFFERENT KINDS OF STEM CELLS
Stem cells are manifold: one typical and standard stem cell does not exist. Once stem cell can produce a multitude of other stem cells, from which organs and tissue are created. Therefore, the terms for stems cells vary.
2 main characteristics are used to differentiate between stem cells: origin and differentiation capacity. A close correlation exists between the two: embryonic stem cells can be described as core cells or pluripotent cells with the ability to form any and all types of tissue structures. These cells are much more versatile than stem cells taken from an adult, but are not used for medical purposed for ethical reasons. Adult stem cells produce cells for individual organs and have the task of regenerating this particular organ. These cells are invaluable in the medical field and are used to treat a variety of disorders and illnesses.
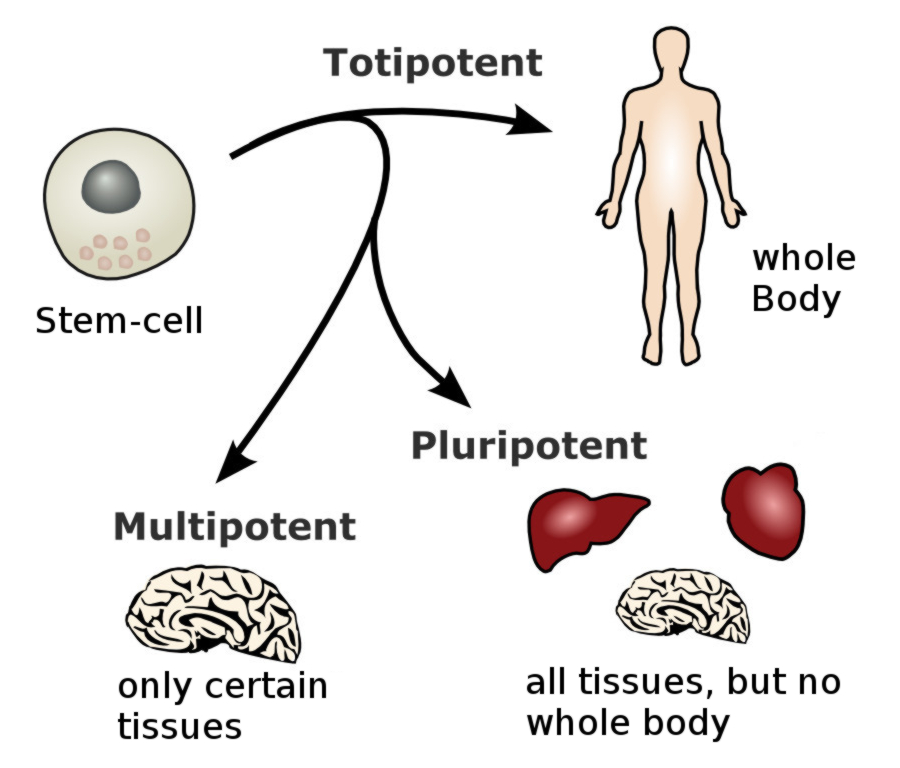
In addition to adult and embryonic stem cells, which are categorized according to their origins, medical science also distinguishes between the capabilities of individual stem cells; these cells are known as totipotent, multi-potent, and pluripotent stem cells. Further distinctions are made between induced pluripotent stem cells (IPS cells) and mesenchymal stem cells. Following is a short description of the different types of stem cells.
ADULT AND EMBRIONAL STEM CELLS
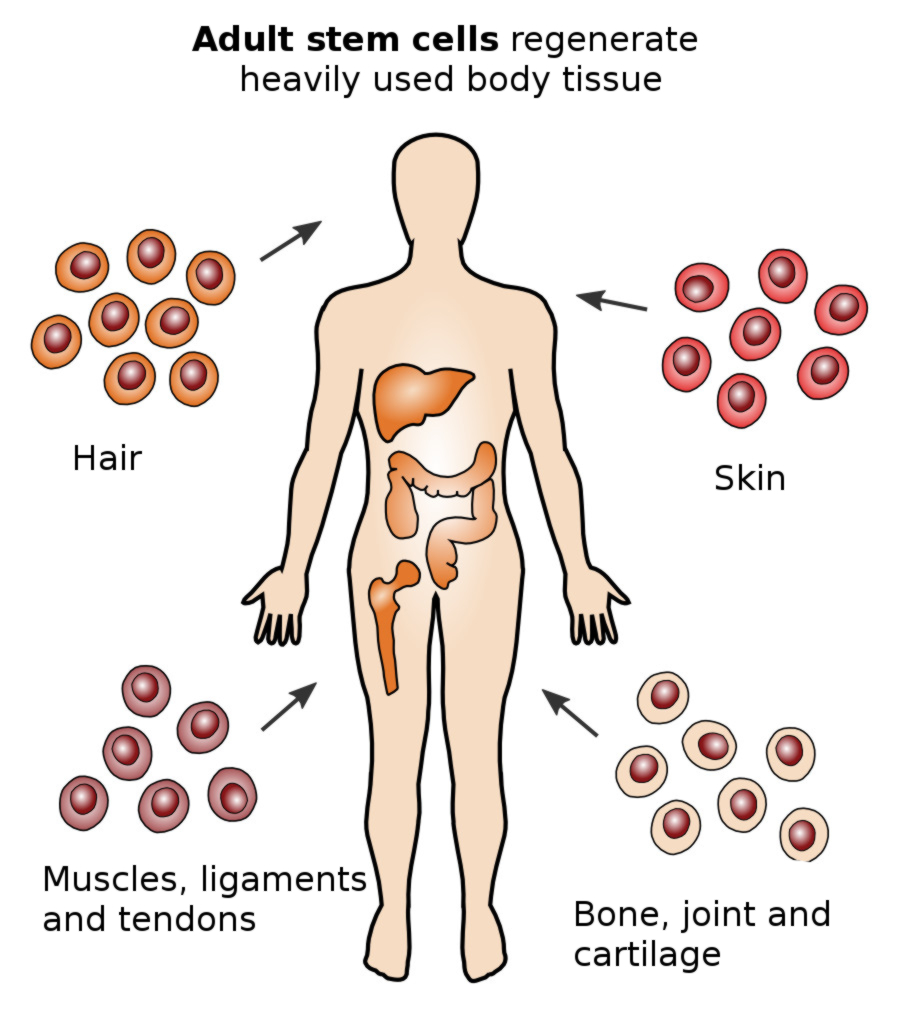
Adult stem cells can be found in the organs of every adult, from birth to an advanced age. These cells are responsible for the regeneration of specific types of body tissue and ensure that the human body remains alive and healthy. Each organ in the human body experiences daily degeneration and must be repaired on a regular basis. For example, the skeleton and muscles degenerate in nearly weekly cycles and are regenerated by stem cells. During the course of a lifetime, this process slows significantly. A young body heals and regenerates quickly, but this process becomes increasingly sluggish as the aging process accelerates. Treatment with stem cells supports the healing process when disorders or illnesses arise.
Embryonic stem cells are found in the earliest development stages of the embryo. These cells grow rapidly and can continue development into any other sort of body tissue or cells. Therefore, these cells are invaluable for scientific research. However, treatments using embryonic stem cells are forbidden for ethical reasons, as cells must be taken from an embryo in order to do so. When speaking about a course of treatment with stem cells at the Center for Regenerative Medicine and Stem Cell Therapy, we are referring exclusively to adult stem cells.
TOTI-, MULTI- UND PLURIPOTENT STEM CELLS
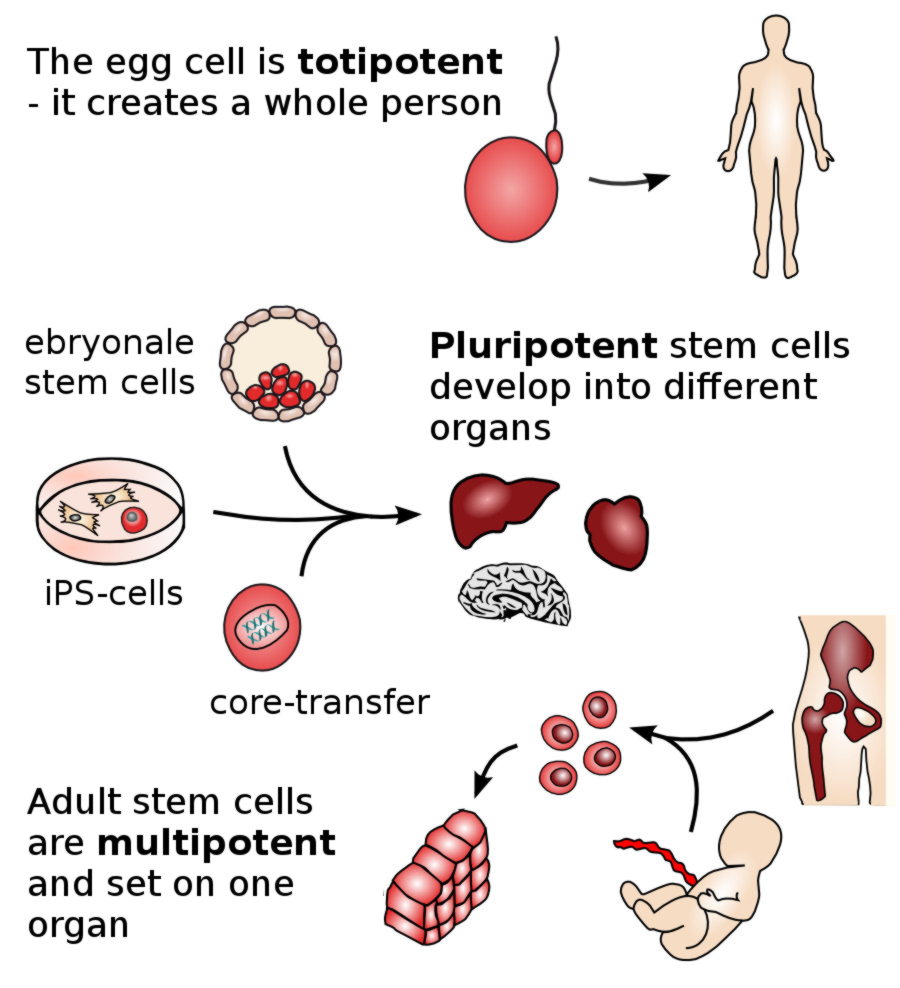
Different sorts of stem cells are characterized by their origin and their ability to develop new tissue and cells. Therefore, not all types of stem cells are useful for medical purposes. At conception, the zygote (also known as the original or prime stem cell) is created. This type of cell carries the ability to develop into a complete human organism and is therefore classified as a totipotent stem cell.
Approximately 5 days after conception, a blastocyst develops, which embeds itself into the lining of the uterus. At this stage, embryonic stem cells can be collected. Embryonic stem cells have the ability to develop into any sort of human tissue or cell, but can no longer express into a complete human organism. These cells are therefore known as pluripotent stem cells.
At birth, stem cells also receive a new nomenclature. These cells are no longer referred to as embryonic stem cells, but are now called adult stem cells. Adult stem cells can develop into diverse organs and are responsible for the maintenance and regeneration of these organs. Due to their capacity to create different sorts of tissue, these cells are known as multi-potent stem cells. This type of cell has been in use in the medical field for quite some time and is harvested from bone marrow or blood taken from the umbilical cord at birth. As these cells are not readily accessible, possibilities for therapeutic use were limited. Clinical and scientific studies have now shown that multi-potent stem cells are found in human adipose tissue in large numbers and may be accessed easily. Therefore, modern stem cell therapy makes use of this type of stem cell, harvested from human adipose tissue, to treat and heal a plethora of disorders and illnesses.
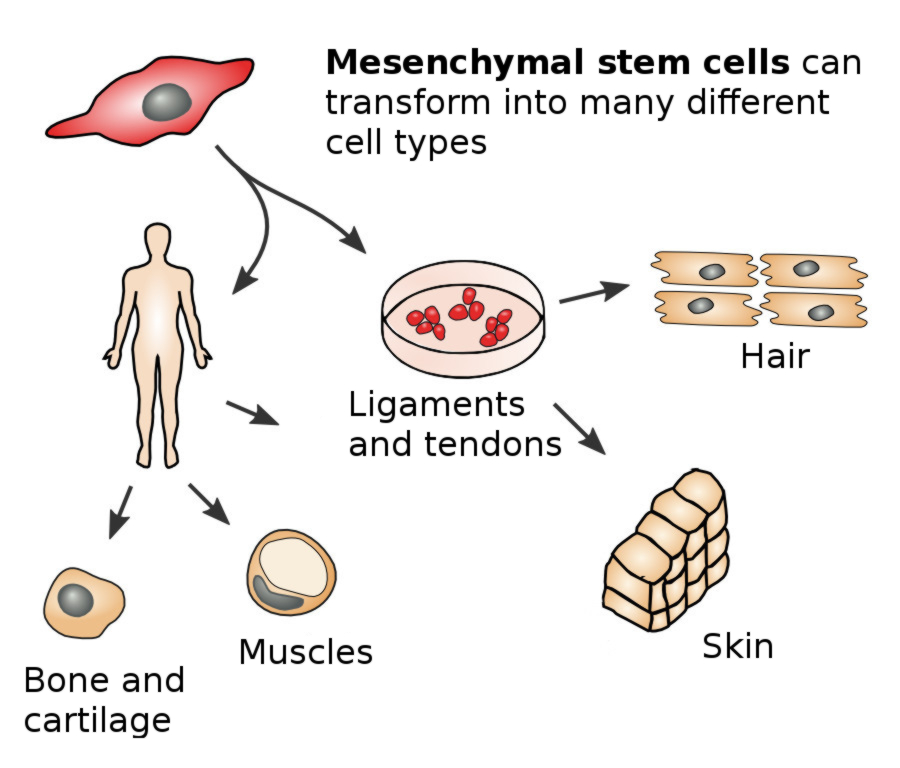
MESENCHYMAL STEM CELLS
Mesenchymal stem cells are a specialized form of adult stem cells. These cells can be isolated and won from bone marrow, cartilage, adipose tissue, muscles, the liver, blood and amniotic fluid. However, the majority of mesenchymal stem cells can be found in adipose tissue, which can be accessed easily via liposuction for therapeutic and medical purposes, in a procedure causing little inconvenience for the patient.
Mesenchymal stem cells have a wide potential range for differentiation and display pluripotential characteristics. Among other functions, these cells are responsible for the regeneration of bones, cartilage, muscles, ligaments and tendons. In addition, these cells have a pronounced anti-inflammatory effect and combat infections. Due to this redoubled positive effect, these cells are highly valued for use in therapeutic treatments and play an important role in the field of arthrosis treatment and therapy. Clinical studies show that in many cases of joint diseases or disorders, wear and tear on the joint is not the cause of pain and discomfort; instead these symptoms are caused by inflammation within the joint itself. In particular painful and chronic diseases of the musculoskeletal system in the shoulders, back, hips knees and hands caused by inflammation or infections can be successfully treated via stem cell therapy using mesenchymal stem cells.
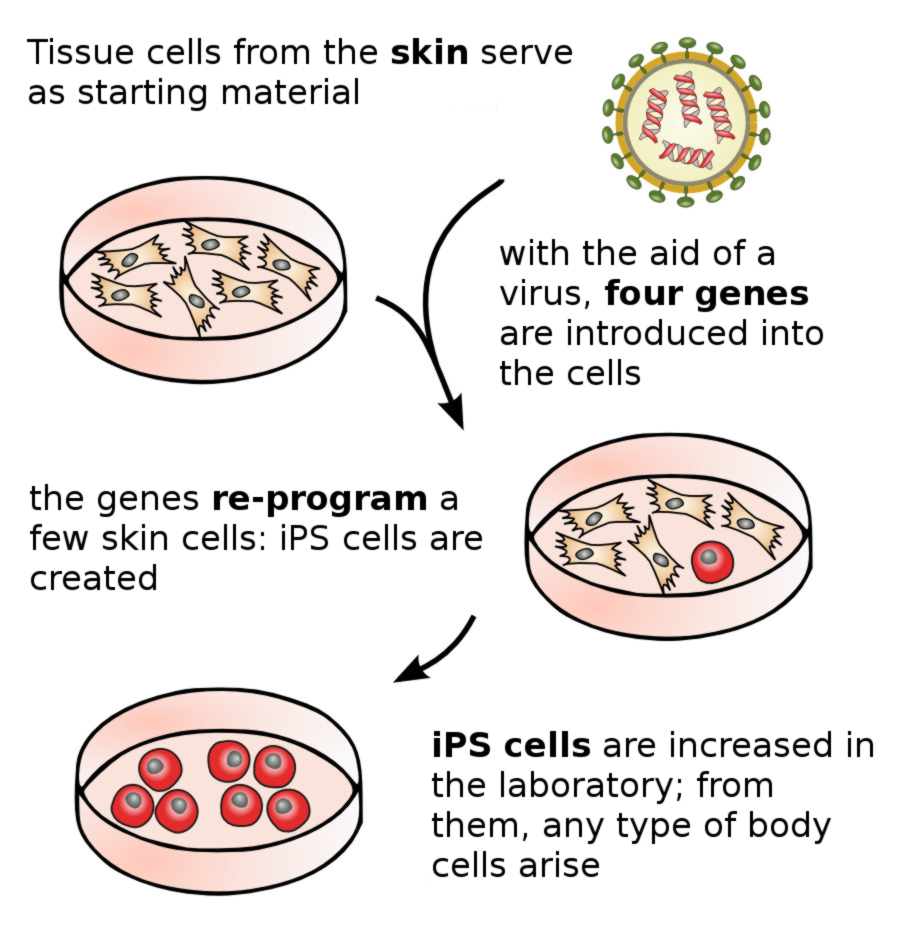
INDUCED PLURIPOTENT STEM CELLS (IPS CELLS)
A specialized category of stem cells is known as induced pluripotent stems cells (IPS stem cells). These stem cells are created via the introduction of 4 genes to previously differentiated adult stem cells, whereby a type of stem cell results which can form any type of tissue or cell, thus displaying significant characteristics of pluripotent stem cells. For the purposes of research and development, these results open up a broader field of opportunities to develop new therapeutic methods for the treatment of numerous diseases and disorders.